Đánh giá tính hiệu quả LLMs Opensource Model, Sizing cần thiết, Định hướng RND.
· 5 min read
1. Executive Summary
Objective
- Evaluate the effectiveness of DeepSeek models, including:
- Reliability
- Response time
- Model suitability per agent type
- Optimize cost and resource sizing
- Assess usage feasibility
Key Findings
- DeepSeek models provide strong performance when used with proper configuration and alignment to task type.
- High-end models (70B+) require expensive infrastructure and should be carefully evaluated for ROI.
- Smaller distilled models can achieve practical efficiency and reliability when tuned correctly.
Impact
- Improved agent reliability and response time
- Flexible deployment options (local/private inference)
- Cost-effective sizing strategies and modular flow architecture
2. Introduction
Background
Current Needs
- Need for private deployable models
- Suboptimal performance on CPU
- Lack of full testing across models and tasks
Challenges
- Too many model options to benchmark exhaustively
- Risks include:
- Slow response times
- Inaccurate outputs (especially with 7B models)
- Difficulty in measuring efficiency
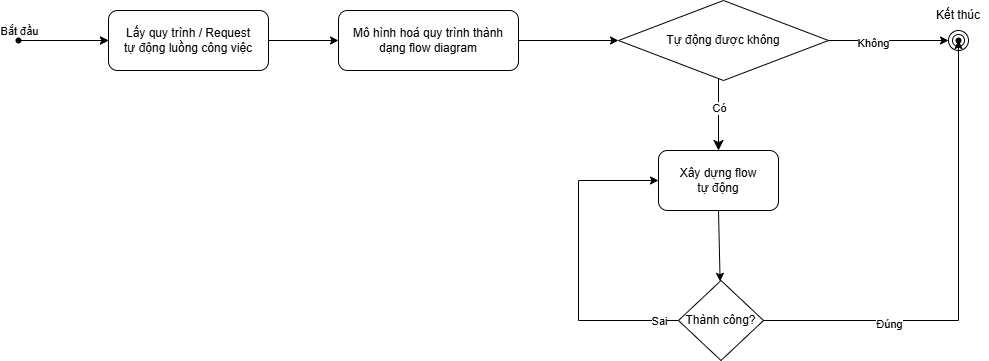
Proposed Solution
- Benchmark and test candidate models
- Use model classification and evaluation metrics
Purpose
- Create a measurable framework for evaluating models
- Classify model capabilities, usage limits, and costs
- Select 3 high-reliability agents for further testing
- Explore optimization strategies for agents
- Propose reliability enhancement techniques
Reference:- Secure data access and privacy
- Improve user experience
Scope
- Conduct a controlled evaluation (no production deployment yet)
- Provide a test suite and benchmarking guidance
3. Research Methodology
Approach
Usage & Environment
- Environment: Ollama, SGLang (ref)
- Tools: Ollama, Langchain, n8n (prebuilt SDK available)
Tested Model Variants
- DeepSeek-V3 (General-purpose)
- DeepSeek-R1 (Reasoning tasks)
- DeepSeek-VL2 (Image+Text)
- Janus (Multi-modal)
- DeepSeek-Coder (Code-focused)
Evaluation Metrics
- Total duration
- Load duration
- Prompt evaluation (count, duration, rate)
- Overall evaluation (count, duration, rate)
Hardware Sizing Reference
Usage: 8hrs per day, on demand:
- Usage for research, application oriented.
- For training model, usage when monthly rent.
| Model Parameters (Billions) | Params (B) | VRAM (GB) | Recommended GPU | CPU Recommendation | RAM (GB) | Price |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 700B | 671 | 1342 | 16x NVIDIA A100 80GB | AMD EPYC 9654 / Intel Xeon Platinum 8490H | 2048+ | 2500$ |
| 14B | 14 | 6.5 | RTX 3080 10GB | Ryzen 9 7900X / i9-13900K | 64+ | N/A |
| 32B | 32 | 14.9 | 1 x A6000 | Threadripper 7980X / Xeon W9-3495X | 128+ | N/A |
| 70B | 70 | 32.7 | 1 x H100 | EPYC 9654 / Xeon Platinum 8490H | 256+ | 1200$ |
4. Analysis and Findings
Benchmark Environment
Configs Used
- Dual RTX 5070Ti: 32GB VRAM, 64GB RAM, i5-14600KF (~$0.5/hr)
- H100 NVL (single): 94GB VRAM, 100GB RAM, EPYC 9354 (~$2.5/hr)
- Dual H100 NVL (~$5/hr)
Model Benchmarks
- llama3.1 (70B): General-purpose
- DeepSeek-R1 (32B, 70B): For reasoning, solution generation
- DeepSeek-Coder (33B): For code explanation/suggestions
- DeepSeek-LLM (67B): General-purpose
Observations
- RTX 5070Ti can handle up to 32B models with tuning; ideal for narrow-scope agents (e.g., coding assistants).
- For 70B models, 5070Ti setup is slow (up to 4 mins response).
- H100 NVL is optimal for real-time inference with 70B+ models.
- Larger models (700B) are currently impractical for cost and infra reasons.
Model Comparison Insights
- 1x A6000 is sufficient for 32B models with proper prompt tuning.
- 1x H100 can support 70B models for testing/research.
- Models with vision capabilities require pre-processing: PDF → Text → Embedding → Vector DB → Retriever → LLM.
- Multi-model workflows (e.g., classification + reasoning) improve accuracy and performance:
User → Model 1 (classifier/tuner) → Model 2 (responder) → Output
5. Use Case Applicability
Suitable Use Cases
- Domain-specific AI agents (e.g., code generation, Q&A bots)
- Parallel model inference to boost reliability
- On-prem inference for sensitive data handling
- Coding support agents
Limitations
- GPU-dependent
- Lacks native image/PDF input unless extended with external modules
- Large model cost constraints
Integration Feasibility
- High if using LangChain/n8n SDKs
- Moderate effort for on-prem setup (requires infrastructure and monitoring)
6. Cost-Benefit Analysis
Implementation Costs
- GPU rental via Vast.ai for prototyping (~$0.5 to $4/hr)
- Setup and tuning time
- DevOps and monitoring for production use
ROI & Savings
- Local inference = no token cost (vs. OpenAI)
- Smaller tuned models yield significant savings
- Modular flows reduce infrastructure duplication
Risks
- Over-investing in large models without maximizing smaller ones
- Long response times = poor UX
- Lack of model support for some input types (e.g., images)
7. Recommendations
Adoption Plan
- Build and tune agents first
- Start with 1x H100 or A6000
- Adopt flow-based architecture:
- Use multiple models for task specialization
- Consider unsupervised learning and prompt chaining
Training & Support
- Document setup and tuning best practices
- Evaluate in-house vs. external support
Further Research
- Model tuning for cost-efficiency
- Explore hybrid models (reasoning + coding)
- Improve model interaction reliability
8. Conclusion
Summary
- DeepSeek offers strong performance when deployed with appropriate infrastructure.
- Smaller models (14B–32B) provide good results with tuning.
- 700B+ models are not cost-effective currently - can not use all the powers yet.
Final Recommendation
- Use 1x A6000 or H100 for research and mid-sized deployments.
- Optimize agent design and build modular flows.
- Focus on maximizing potential of 32B models before scaling up.